
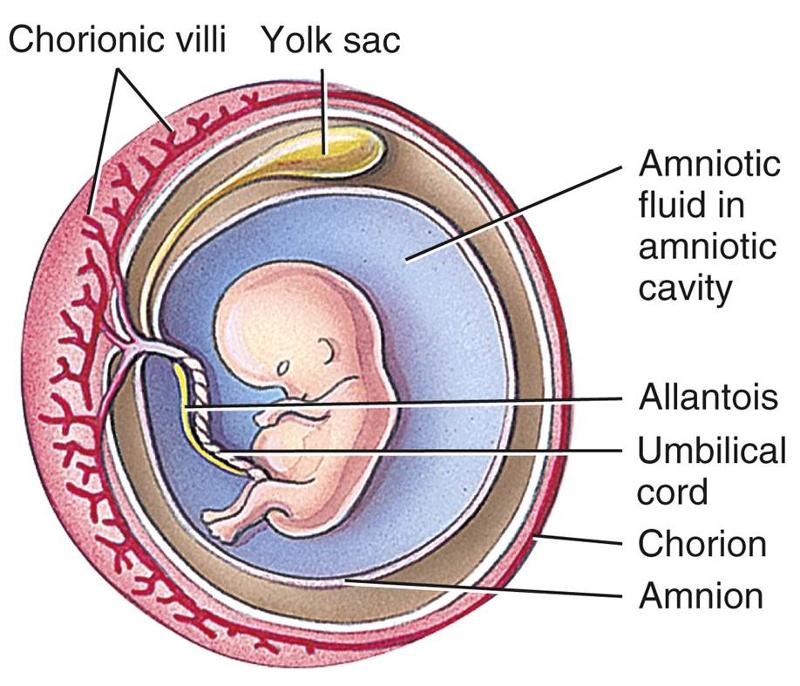
This leads to excessive urination by the fetus, thereby causing an increase in the amniotic fluid.
 Uncontrolled diabetes in the mother causes an increase in the level of fetal blood sugar. It leads to excessive secretion of amniotic fluid. Placental causes: A tumor of the placenta called chorioangioma causes polyhydramnios. It may occur due to Rh blood mismatch between the mother and the fetus, or several other problems The more excess amniotic fluid there is the greater the severity of polyhydramnios. Hydrops fetalis, where there is an accumulation of fluid in two or more areas of the fetus like the scalp, around the lungs and heart, and in the abdominal cavity. Inability of the fetus to swallow amniotic fluid due to facial clefts, neck masses and developmental problems of the food pipe and the duodenum, the first part of the intestine. Neural tube defects which result in conditions like anencephaly, where the brain is not developed, and openspina bifida, a Birth Disorder, where the spinal cord is not well developed. Some of the most common causes of polyhydramnios are as follows: Maternal diabetes: Diabetes, including gestational diabetes, can lead to amniotic fluid. It is the opposite of oligohydramnios, a condition in which there is an insufficient level of amniotic fluid. Genetic abnormalities like abnormal number of chromosomes Polyhydramnios, an excess of amniotic fluid, occurs in about 1 of pregnancies. Fetal causes: Since the fetus normally swallows amniotic fluid, fetal malformations are associated with polyhydramnios. Polyhydramnios is a medical condition in pregnant women where an excess of amniotic fluid occurs in the amniotic sac. In others, polyhydramnios may be due to fetal, maternal or placental causes. a fatty substance that covers fetus and neonates skin. In many cases, the cause of polyhydramnios is not known. Echogenic amniotic fluid can be seen in normal pregnancies 2,5 but can also be seen in association with various conditions 1-5 : First trimester : hemorrhage into the amniotic cavity.
Uncontrolled diabetes in the mother causes an increase in the level of fetal blood sugar. It leads to excessive secretion of amniotic fluid. Placental causes: A tumor of the placenta called chorioangioma causes polyhydramnios. It may occur due to Rh blood mismatch between the mother and the fetus, or several other problems The more excess amniotic fluid there is the greater the severity of polyhydramnios. Hydrops fetalis, where there is an accumulation of fluid in two or more areas of the fetus like the scalp, around the lungs and heart, and in the abdominal cavity. Inability of the fetus to swallow amniotic fluid due to facial clefts, neck masses and developmental problems of the food pipe and the duodenum, the first part of the intestine. Neural tube defects which result in conditions like anencephaly, where the brain is not developed, and openspina bifida, a Birth Disorder, where the spinal cord is not well developed. Some of the most common causes of polyhydramnios are as follows: Maternal diabetes: Diabetes, including gestational diabetes, can lead to amniotic fluid. It is the opposite of oligohydramnios, a condition in which there is an insufficient level of amniotic fluid. Genetic abnormalities like abnormal number of chromosomes Polyhydramnios, an excess of amniotic fluid, occurs in about 1 of pregnancies. Fetal causes: Since the fetus normally swallows amniotic fluid, fetal malformations are associated with polyhydramnios. Polyhydramnios is a medical condition in pregnant women where an excess of amniotic fluid occurs in the amniotic sac. In others, polyhydramnios may be due to fetal, maternal or placental causes. a fatty substance that covers fetus and neonates skin. In many cases, the cause of polyhydramnios is not known. Echogenic amniotic fluid can be seen in normal pregnancies 2,5 but can also be seen in association with various conditions 1-5 : First trimester : hemorrhage into the amniotic cavity.








